Design thinking is a methodology that facilitates problem solving and the design and development of all sorts of products and services in a concrete context. It is used by highly motivated teams that have innovation and creativity at their core. Another foundation of design thinking is that it is focused on human beings. It is therefore also commonly known as human-centred design.
The main principles of design thinking:
A number of principles are critical to design thinking and are reflected in the methodology:
Empathy for the user
Design thinking is defined by coming up with solutions that meet the needs of real humans and respond to user feedback. People, rather than technology, are the driving force of innovation.
Collaboration
Design thinking brings together heterogeneous and multi-disciplinary teams that do not usually work together.
Plenty of brainstorming
Design thinking is a solution-based methodology. As such, the attention is on generating plenty of ideas and potential solutions, encouraging participants to come up with lots of ideas, rather than worrying about the quality of them.
Experimentation and iteration
But it’s not all just about ideas. The ideas are made into prototypes that are tested and then tweaked based on user feedback. This is an interactive way of working.
Action
Rather than formulating hypotheses about what users want, design thinking encourages you to get out and about and interact with them. This helps you to turn ideas into tangible prototypes and test them in real-life situations.
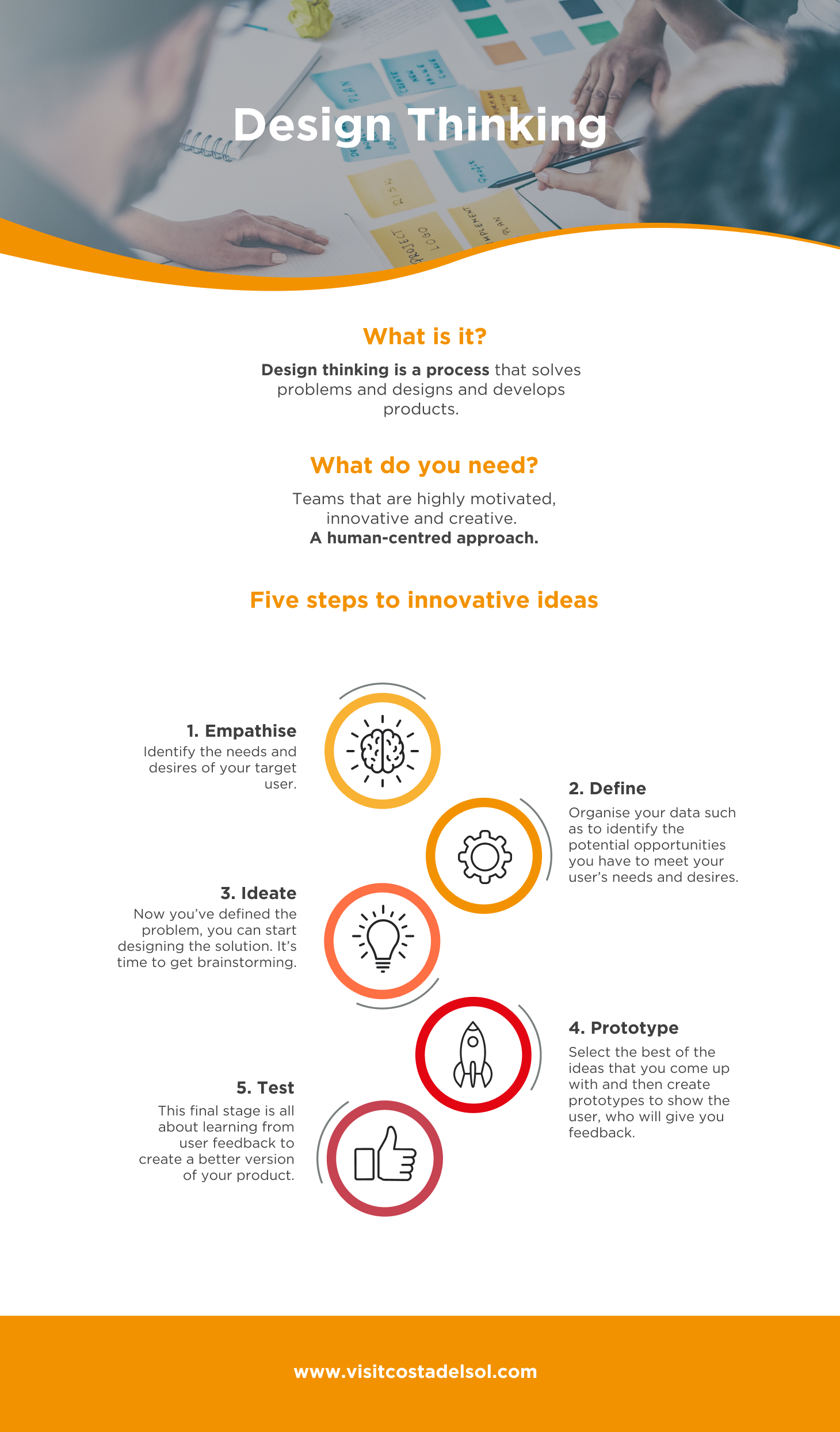
The design thinking process: step by step
The popularity of design thinking lies in its ability to come up with innovative solutions in a very short space of time. It is a methodology that entrepreneurs and start-ups can use to push forward and quickly test hypotheses, creating a culture of creativity and innovation within companies. The main stages of the design thinking process are as follows.

Empathise
This is the first step in the design thinking process and, in a certain sense, is what it’s all about. The aim is to identify the needs and desires of the user. To do so, you must determine your target audience, set out your research goals and decide how information will be collected. Some examples of information collection techniques at this stage involve in-depth interviews, observation, focus groups, etc.
Define
The second stage of the design thinking process involves organising all the information you have gathered such as to extract all the potential opportunities you have to create solutions to the needs and desires of your users. Once you have done this, you should be able to come up with a “problem statement” that explains the problem in a human-centred manner. For instance, “what we can do to (+ problem statement)”.

Ideate
Once you have clearly set out the problem, it’s time to start thinking about a solution to it. The ideate stage involves coming up with as many ideas as possible. To do so, brainstorm and then brainstorm some more to come up with plenty of potential solutions.
Prototype
You can now select the best of the ideas that you came up with in your brainstorming session and prototype them. This basically consists of bringing your ideas to life so you can show them to the user. They, in turn, will give you feedback of whether the solutions really meet their needs and desires. There are many different ways to prototype, such as concept testing, storyboards and mockups.

Test
Of all the stages in design thinking, the last is probably the most important: it is time to present your prototype to the potential user. It is important to remember that at this stage you are not selling a product: you are seeking to learn from the user’s feedback to then make it even better.
Design thinking is a powerful tool in product and service design. It’s incredibly useful for entrepreneurs and start-ups as it enables them to make progress quickly. Have you ever used the methodology? If not, what are you waiting for?!